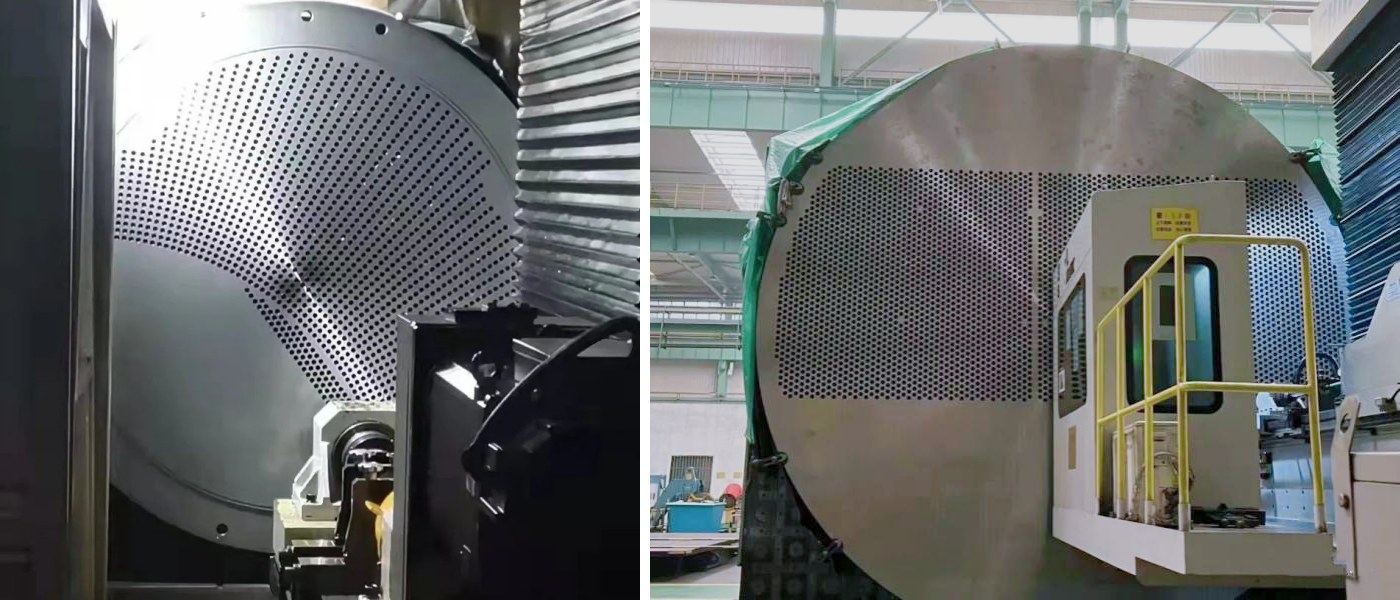
What Are You Looking For?
Heat exchanger is a widely used equipment in fields such as chemical, petroleum, and energy. A heat exchanger is a heat exchange device used for fluids with temperature differences. There are at least two types of fluids in the heat exchanger, with higher temperatures releasing heat and the opposite absorbing heat. Therefore, the tube pattern of tube sheet is particularly important, as the arrangement of tube bundles directly affects the performance and efficiency of heat exchangers. The following is a detailed introduction to the tube pattern of tube sheet:

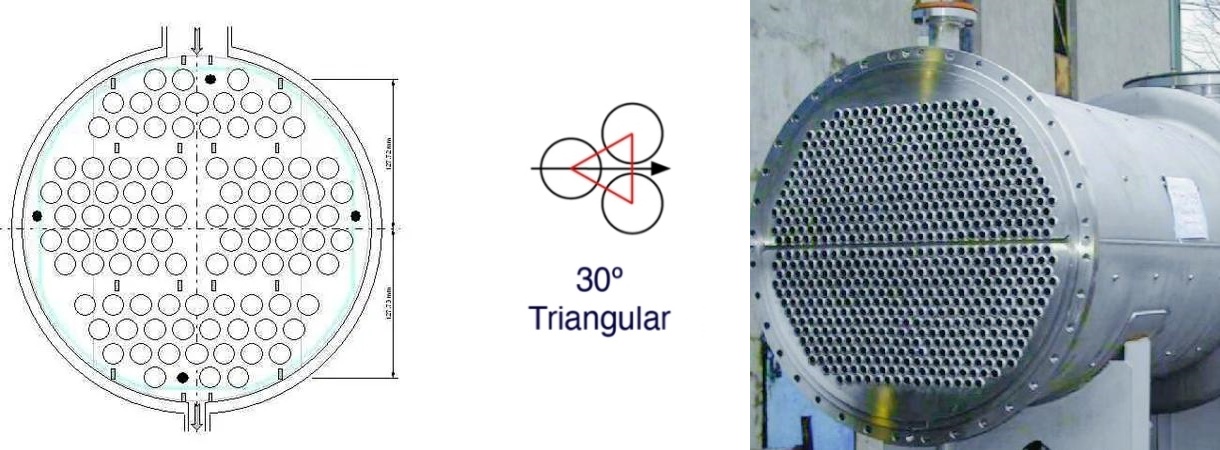
1. 30° Triangle
Triangle is a common arrangement of tube bundles. The centerline of each pipe forms an equilateral triangle with the centerline of two adjacent pipes, with one side of the triangle perpendicular to the flow direction. This arrangement has the following advantages:
Large heat transfer area: Compared with a square pattern, the spacing between heat exchange tubes in a regular triangle arrangement is equal, so a large number of tubes can be arranged on the same tube sheet area, resulting in a higher heat transfer coefficient and an improved heat transfer rate.
Low fluid resistance: Due to the small gap between pipes, the resistance of fluid flow between pipe bundles decreases, which is beneficial for fluid flow.
Simple structure: The arrangement of the equilateral triangle is simple, which can save about 15% of the tube sheet area, and is convenient for marking and drilling the tube sheets of the column heat exchanger, making it easy to manufacture and install.
However, this arrangement makes it difficult to clean the heat exchange tubes, making it suitable for conditions where there is no fouling or chemical methods can be used to clean the fouling, as well as allowing for high pressure drop. It should be noted that when mechanical cleaning is required for the shell side, a triangular arrangement should not be used.
2. 60° Rotated Triangle
Rotated triangles are an improved arrangement of regular triangles. The centerline of each pipe forms a triangle with the centerline of two adjacent pipes, with one side of the triangle parallel to the flow direction. This arrangement has the following advantages:
High heat transfer efficiency: Due to the opposite direction of the inlet and outlet of the pipe, the flow time of the fluid inside the pipe is prolonged, thereby improving the heat transfer efficiency.
Uniform distribution of hot fluid: Due to the opposite direction of the inlet and outlet of the pipe, the hot fluid can be fully mixed inside the pipe, making the distribution of hot fluid more uniform.
Its characteristics lie between the arrangement of equilateral triangles and squares. Due to the gradually thickened condensate film formed on the outer surface of the bottom heat exchange tube, heat transfer is weakened. Therefore, it is not suitable for horizontal condensers, but is easy to clean mechanically. It is commonly used in floating head heat exchangers where the shell side medium is prone to fouling. The inter tube channel should be continuous along the entire tube bundle and ensure a 6mm cleaning channel. At the same time, in rod supported longitudinal flow heat exchangers, this arrangement is often used to facilitate the discharge of baffle rods.

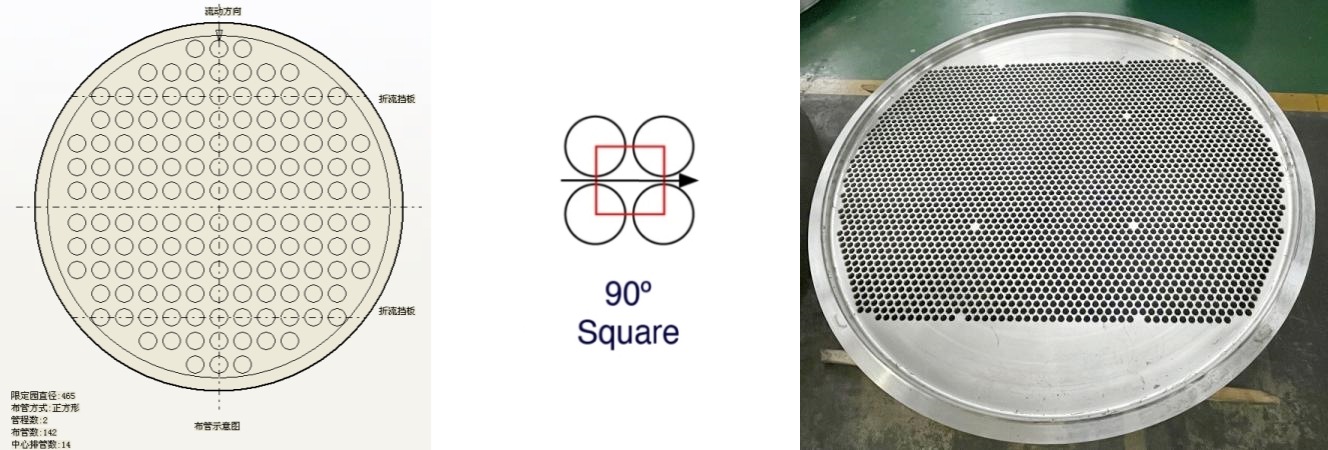
3. 90° Square
90° square is the arrangement of pipes in a square shape on the tubesheet, forming a parallel arrangement with the coordinates of the pipes. The advantage of this arrangement is that it is clear and easy to locate and maintain pipelines, making it more suitable for equipment that requires frequent cleaning and maintenance. In addition, due to the large distance between pipelines, pressure loss will also be correspondingly reduced, and the stability and durability of the equipment will be higher. However, compared to the triangular arrangement, the density and heat transfer efficiency of the pipe network formed by the square arrangement are relatively low.
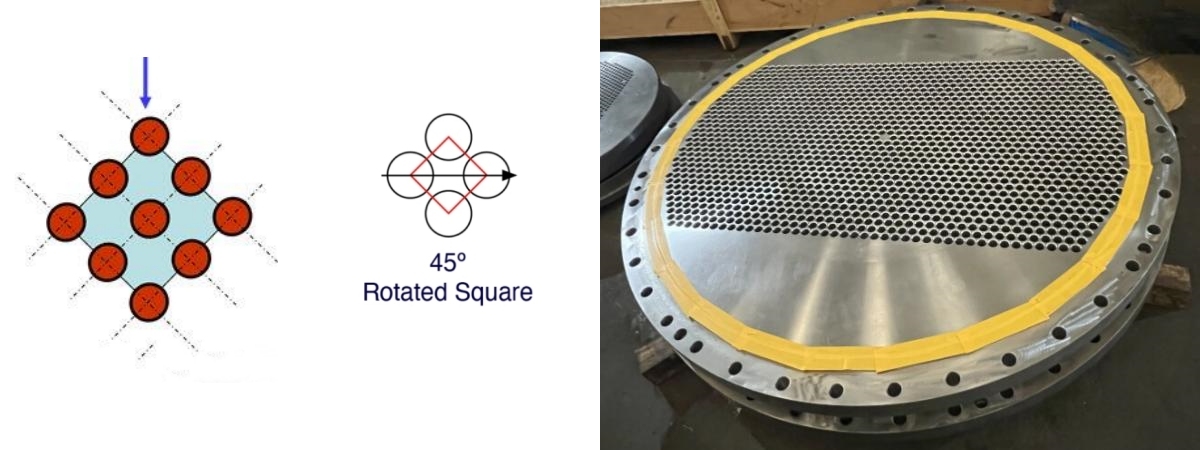
4. 45° Rotated Square
45° Rotated Square is a relatively less commonly used arrangement of heat exchange tubes. Its characteristic is to arrange the pipes in a diamond grid, so that the cold and hot media appear alternately at the four corners of the diamond. The advantage of this arrangement is that the pipeline layout is compact, occupying an extremely small area of the pipe plate, making it suitable for equipment with smaller device areas. In addition, the diamond arrangement also helps to improve the heat transfer efficiency of the equipment and can effectively reduce the temperature difference of the medium. The disadvantage is that for equipment using this method, maintenance and cleaning are relatively difficult, which can easily lead to pipeline blockage and damage.
It is worth noting that (1) the arrangement of equilateral triangles and angular squares is called staggered arrangement in heat transfer, which can form turbulence when the medium flows and is beneficial for heat transfer; The arrangement of corner triangles and squares in heat transfer is called a straight line, and a part of the medium flow is laminar, which has an adverse effect on heat transfer. Therefore, for heat exchangers without phase change, it is advisable to use a regular triangle or corner square arrangement; For condensers with phase change, corner triangle and square arrangements can generally be used. (2) For multi tube heat exchangers, the combination arrangement method can be used. Each section is arranged in a regular triangle, and the sections are arranged in a square shape to facilitate the arrangement of dividing sections.
